3 releases
| 0.1.2 | Apr 5, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.1 | Sep 17, 2022 |
| 0.1.0 | Sep 13, 2022 |
#246 in Text editors
125KB
1K
SLoC
jot
Installation • Usage • Notes • Changelog • Build from Source • Dependencies • Authors • License
Jot is a feature-stripped version of Obsidian focused on rapid note management through the terminal.
It uses the same format of storage as Obsidian, i.e. markdown files for notes, and local folders for vaults (and sub-folders).
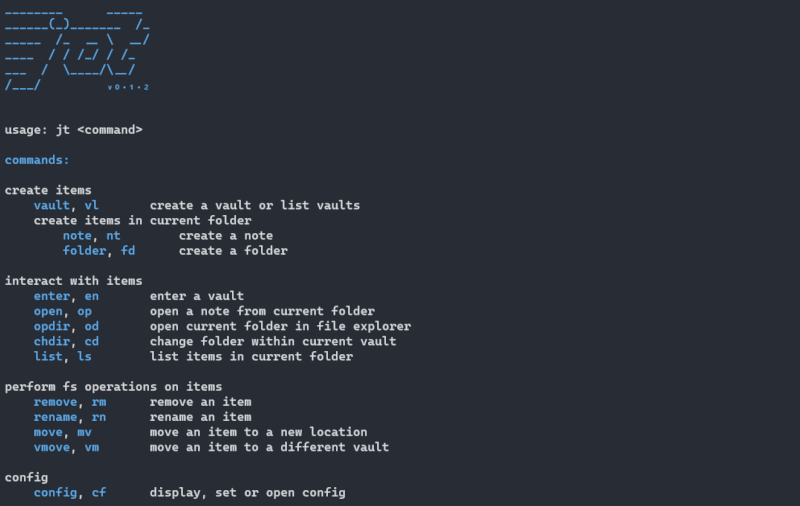
Commands that encompass all basic needs are included. Each command has an alias (two letter abbreviation) to further increase rapidity.
Installation
Install with cargo:
$ cargo install jt
Use executable (only for windows)
Download jt.exe (v0.1.2) and add it to your path.
Usage
The following example represents a general user flow when first using Jot.
Create a vault using the following command:
$ jt vault newvault ~/vaults
Here, newvault is the name of the vault, and '~/vaults' is the location where it will be created (this location should be an absolute fs path and exist already or jot will throw an error).
Providing no arguments to vault command will list all vaults.
$ jt vault
Adding the '-l' flag will list all vaults with their locations.
$ jt vault -l
At this moment only newvault will be listed.
Enter into the vault:
$ jt enter newvault
enter command is also used to switch to other vaults.
Create notes and folders:
$ jt note newnote
$ jt folder newfolder
note and folder, both work similarly and create the corresponding items in current folder. When a vault is first created, the current folder is set to its root.
Open a note:
jt open newnote
open command will open the specified note with the editor set in config.
Change folder:
$ jt chdir newfolder
chdir command will switch the current folder to the location mentioned.
Relative path to location from current folder has to be provided. Standard fs paths are accepted as valid input, like '../folder1/somefolder/'.
$ jt chdir ..
This will switch back to the root of vault.
Open current folder in explorer:
$ jt opdir
opdir command will open the current folder in the default file explorer.
List items in current folder:
$ jt list
When needed list command will print the dir tree of current folder.
All notes will be highlighted in blue ![]() .
.
This is what the dir tree will look like with this vault's root as the current folder.
newvault
├── newfolder
└── newnote # highlighted in blue
Adding an item type (note or folder) to the list command like so,
$ jt list note
will only list items of the specified type.
Fs operations:
Command remove works as its name suggests, on all items (vault, note, or folder).
$ jt remove note newnote
Commands rename and move are used similarly but take one additional argument each.
Command rename takes the new name as its third argument.
$ jt rename note newnote somenewnote
Command move takes the new location as its third argument.
For vaults, path rules are same as vault command and for other items, path rules are same as chdir command.
$ jt move note newnote /newfolder/
These commands take the item type (vault, note, or folder) as their first argument.
Command vmove is similar to move, but it moves an item (note or folder) from the current folder of the current vault to the root of a different vault, and takes the name of this vault as an argument in place of location.
$ jt vmove note newnote somevault
Every keyword used so far (commands and item names) is interchangeable with its two letter alias, e.g. move command can also be written as:
$ jt mv nt newnote /newfolder/
Handle Jot's config:
$ jt config
config command will open the config file in the set editor. By default this is nvim.
Specifying a config field as an argument will display its value without opening the config file itself.
$ jt config editor
Providing a value as an additional argument will update the field.
$ jt config editor code.cmd
Get Help
Run jt without a command, or with help command or -h flag for main help message.
$ jt
Use help command or -h flag with a command to get corresponding help.
$ jt help vault
$ jt vault -h
Notes
General
- Jot is published on crates.io as 'jt', since 'jot' wasn't available.
- As of now, Jot has only been tested on windows (and WSL).
Config & Data
- App data is stored in config and data files in locations generated by the directories crate. Individual Vault data is stored in '.jot' folder inside each vault. It is advised that these files not be tampered with, since atm there's no way to automatically fix them.
- App data files are generated in their default state the first time a command is run, if they don't exist already. Vault data files are generated in their default state when a vault is created.
- App config has two fields: editor & conflict.
- editor by default is set to nvim and conflict to true.
- conflict field tells jot if the editor conflicts with it for control over the terminal. Set it to true for editors like nvim and false for editors like notepad.
Changelog
-
v0.1.2 :
-
Fix:
listcommand could display items other than notes and folders.- process_path() couldn't collapse certain paths properly, and std::fs::canonicalize doesn't work as intended on windows. dunce crate has been used to achieve the required function.
-
Feat:
opdircommand has been added to enable opening the current folder in the default file explorer.listcommand can now filter items based on the item type provided.configcommand can now open the config file in the set editor.
-
-
v0.1.1 :
- As advised by u/epage (github/epage) on my r/rust post, commands are now represented by their full word, and the two letter abbreviations (previously serving as commands themselves) are now aliases for these commands.
- Updated docs.
Build from Source
Prerequisites
- Git is need to clone the repository on your machine.
- Cargo is needed to compile the program.
Build
Clone the repo and cd into the directory:
$ git clone https://github.com/araekiel/jot.git
$ cd jot
Run the following command to install dependencies and build/compile the program.
$ cargo build
Then run the executable created in 'target/debug/' (or add it to your path).
Or, run the tool directly:
$ cargo run -- *args*
Pass in commands and arguments after '--'.
Dependencies
- serde & toml have been used in tandem to read and write data files.
- clap has been used to create the command line interface.
- directories has been used to generate os-dependent config and data file locations.
- fs_extra has been used for recursive move of folders.
- dunce has been used as an alternative to std::fs::canonicalize.
Authors
- araekiel - Github
License
MIT License | Copyright (c) 2023 Kumar Shashwat
Dependencies
~2.1–3MB
~55K SLoC