6 releases
| 0.1.7 | Feb 23, 2025 |
|---|---|
| 0.1.6 |
|
| 0.1.5 | Nov 29, 2024 |
#265 in Cryptography
676 downloads per month
7.5MB
1K
SLoC
ezcheck
ezcheck(easy check) is an easy-to-use, lightweight, cross-platform, and high-performance tool for calculating, comparing, and verifying hash of strings and files. Designed to prevent content tampering and ensure file integrity.
ezcheck have three backends: ring, hashes and mix backend(ring and hashes), and you can only choose one of them. The main differences between them are:
| Features | ring | hashes | mix(Recommended) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast. | About 5 times slower than ring. | Use the fastest backend that supports the algorithm. |
| Supported algorithms | SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, SHA512/256 | MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, SHA512/256 | MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, SHA512/256, XXHASH32, XXHASH64, XXHASH3_64 |
| Implement languages | Assembly, Rust, C and etc.. | Rust | Assembly, Rust, C and etc.. |
| Compatibility | May not work on every machine with different architecture. | Works well with Rust. | Same to ring. |
❗️ To achieve both fastest speed and maximum compatibility, the default backend is mix backend.
⚠️ Please notice that although ezcheck supports a lot of hash algorithms, MD2, MD4, MD5, SHA1 are proven to be
insecure. ezcheck still provides them for maximum compatibility, but it does not recommend users continue to use
them.
Setup
Direct Binary Download
Download the suitable mix backend binary from the release.
Install from Cargo
$ # mix backend
$ cargo install ezcheck
$ # ring backend
$ cargo install ezcheck --no-default-features --features ring_backend
$ # hashes backend
$ cargo install ezcheck --no-default-features --features hashes_backend
Instantly run ezcheck with x-cmd
x-cmd is a lightweight cross-platform package manager implemented in posix shell. Quickly download
and execute ezcheck with a single command: x ezcheck
You can also install ezcheck in the user level without requiring root privileges:
$ x env use ezcheck
Build from source
Build
$ git clone https://github.com/Metaphorme/ezcheck && cd ezcheck
$ # Choose one from mix backend, hashes backend or ring backend
$ # mix backend
$ cargo build --release
$ # ring backend
$ cargo build --release --no-default-features --features ring_backend
$ # hashes backend
$ cargo build --release --no-default-features --features hashes_backend
$
$ ./target/release/ezcheck --version
Run tests
$ git clone https://github.com/Metaphorme/ezcheck && cd ezcheck
$ cargo test # mix backend
$ cargo test --no-default-features --features ring_backend # ring backend
$ cargo test --no-default-features --features hashes_backend # hashes backend
Usage
Supported hash algorithms of different backends:
| ring | hashes | mix |
|---|---|---|
| MD2 | MD2 (hashes backend) | |
| MD4 | MD4 (hashes backend) | |
| MD5 | MD5 (hashes backend) | |
| SHA1 | SHA1 (hashes backend) | |
| SHA224 | SHA224 (hashes backend) | |
| SHA256 | SHA256 | SHA256 (ring backend) |
| SHA384 | SHA384 | SHA384 (ring backend) |
| SHA512 | SHA512 | SHA512 (ring backend) |
| SHA512/256 | SHA512/256 | SHA512/256 (ring backend) |
| XXHASH32 | ||
| XXHASH64 | ||
| XXHASH3_64 |
Calculate
Calculate hash for file(s) or text.
$ # Usage:
$ # ezcheck calculate|c [ALGORITHM (Default SHA256)] (-f file(s)/"-" for standard input | -t text)
$
$ # Examples:
$ ezcheck c sha256 -f image.jpg
b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2 image.jpg
$
$ cat image.jpg | ezcheck calculate sha256 -f -
b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2 -
$
$ ezcheck calculate sha256 -t "Hello"
SHA256: 185f8db32271fe25f561a6fc938b2e264306ec304eda518007d1764826381969
$
$ ezcheck calculate -f image.jpg
No algorithm specified. Using SHA256 as the default.
b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2 image.jpg
$
$ # We could also redirect the output into a file, just like shasum does.
$ ezcheck calculate sha256 -f image.jpg > sha256sum.txt
Compare
Compare with given hash.
$ # Usage:
$ # ezcheck compare|m [ALGORITHM (Leave blank to automatically detect algorithm)] (-f file/"-" for standard input | -t text) -c hash
$
$ # Examples:
$ ezcheck m sha256 -f image.jpg -c b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2
SHA256 OK
$
$ cat image.jpg | ezcheck compare sha256 -f - -c b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2
SHA256 OK
$
$ ezcheck compare sha256 -t "Hello" -c 085f8db32271fe25f561a6fc938b2e264306ec304eda518007d1764826381969
SHA256 FAILED Current Hash: 185f8db32271fe25f561a6fc938b2e264306ec304eda518007d1764826381969
$
$ # Auto detect hash algorithm
$ ezcheck compare -f image.jpg -c b68c5da64847c4d8fd046ea6d6b4739f
INFO: Hash Algorithm could be MD5, MD4, MD2
MD5 FAILED Current Hash: c8d0b68ed0abd920f9388973aa5a926e
MD4 OK
Check
Check with given shasum-style check file.
shasum-style check file could be generated from shasum and ezcheck. It looks like:
00691413c731ee37f551bfaca6a34b8443b3e85d7c0816a6fe90aa8fc8eaec95 滕王阁序.txt
b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2 *image.jpg
$ # Usage:
$ # ezcheck check|k [ALGORITHM (Leave blank to automatically detect algorithm)] -c check-file
$
$ # Warning: The shasum file (or check file) should be in the same directory with files to be checked.
$ # Example:
$ ezcheck k sha256 -c sha256sum.txt
滕王阁序.txt: SHA256 OK
image.jpg: SHA256 OK
$
$ # Auto detect hash algorithm
$ cat md4sum.txt
9ec44ac67ab1e1c98fe0406478d5297d 滕王阁序.txt
b68c5da64847c4d8fd046ea6d6b4739f image.jpg
$ ezcheck check -c md4sum.txt
滕王阁序.txt: MD5 FAILED Current Hash: 07c4e6a2c2db5f2d3a8998a3dba84a96
滕王阁序.txt: MD4 OK
image.jpg: MD5 FAILED Current Hash: c8d0b68ed0abd920f9388973aa5a926e
image.jpg: MD4 OK
$
$ # Actually, ezcheck supports various algorithm in the same check file in auto detect.
$ # 🤔 But why this happens?
$ cat sha256sum.txt
00691413c731ee37f551bfaca6a34b8443b3e85d7c0816a6fe90aa8fc8eaec95 滕王阁序.txt
b4c5e1d0a1f84a07ef6f329d3dcec62bce40103f49d8088e2b1b98a87e4ff0c2 *image.jpg
9ec44ac67ab1e1c98fe0406478d5297d 滕王阁序.txt
$
$ ezcheck check -c sha256sum.txt
滕王阁序.txt: SHA256 OK
image.jpg: SHA256 OK
滕王阁序.txt: MD5 FAILED Current Hash: 07c4e6a2c2db5f2d3a8998a3dba84a96
滕王阁序.txt: MD4 OK
Benchmark
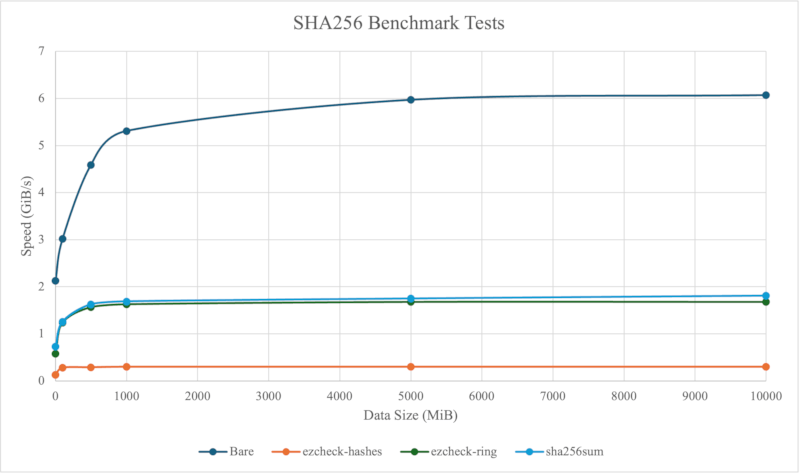
SHA256 Benchmark Tests
Method
-
Device: MacBook Air M1 8GB
-
Steps
-
Run and repeat 3 times:
$ count=10000 # Test size = 1MiB * $count $ # Bare, Speed of generating the data $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=$count | pv > /dev/null $ # ezcheck-hashes $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=$count | pv | ./ezcheck-hashes calculate sha256 -f - $ # ezcheck-ring $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=$count | pv | ./ezcheck-ring calculate sha256 -f - $ # sha256sum $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=$count | pv | sha256sum -
Calculate the average value.
-
Result
| Implementation / Speed(GiB/s) / Test size(MiB) | 1 | 100 | 500 | 1000 | 5000 | 10000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare (Speed of generating the data) | 2.13 | 3.02 | 4.59 | 5.31 | 5.97 | 6.07 |
| ezcheck-hashes | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| ezcheck-ring | 0.58 | 1.24 | 1.57 | 1.63 | 1.68 | 1.68 |
| sha256sum | 0.73 | 1.26 | 1.63 | 1.69 | 1.75 | 1.81 |
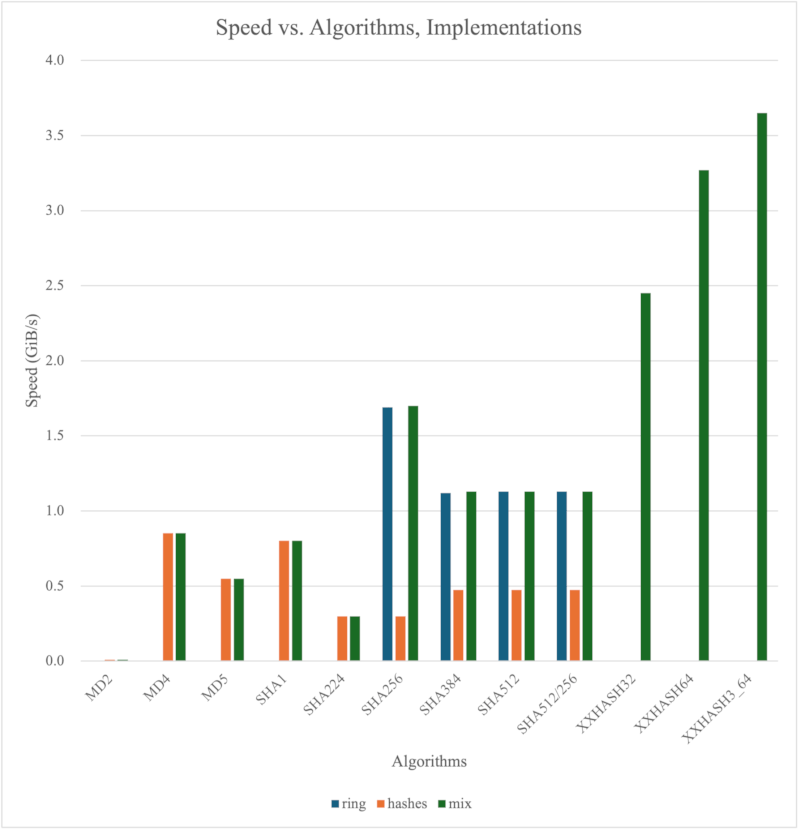
Speed vs. Algorithms, Implementations
Method
-
Device: MacBook Air M1 8GB
-
Steps
- Run:
$ algorithm=sha256 $ # ezcheck-hashes $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=10000 | pv | ./ezcheck-hashes calculate $algorithm -f - $ # ezcheck-ring $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=10000 | pv | ./ezcheck-ring calculate $algorithm -f - $ # ezcheck-mix $ dd if=/dev/zero bs=1M count=10000 | pv | ./ezcheck-mix calculate $algorithm -f - - Calculate the average value.
- Run:
Result
| Algorithms / Speed(GiB/s) / Implementations | ring | hashes | mix |
|---|---|---|---|
| MD2 | null* | 0.00896 | 0.00896 |
| MD4 | null* | 0.852 | 0.852 |
| MD5 | null* | 0.549 | 0.549 |
| SHA1 | null* | 0.802 | 0.802 |
| SHA224 | null* | 0.299 | 0.299 |
| SHA256 | 1.69 | 0.298 | 1.70 |
| SHA384 | 1.12 | 0.473 | 1.13 |
| SHA512 | 1.13 | 0.473 | 1.13 |
| SHA512/256 | 1.13 | 0.473 | 1.13 |
| XXHASH32 | null* | null* | 2.45 |
| XXHASH64 | null* | null* | 3.27 |
| XXHASH3_64 | null* | null* | 3.65 |
null*: The algorithm is not implemented in this implementation.
License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2024 Heqi Liu
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.
Dependencies
~1–10MB
~123K SLoC