43 releases (15 breaking)
| 0.18.1 | Sep 12, 2023 |
|---|---|
| 0.18.0 | May 8, 2023 |
| 0.17.2 | Apr 23, 2023 |
| 0.17.0 | Mar 11, 2023 |
| 0.8.3 | Nov 30, 2022 |
#139 in Concurrency
162 downloads per month
370KB
4K
SLoC
Kueue
A robust, user-level, work-stealing, distributed task scheduler.
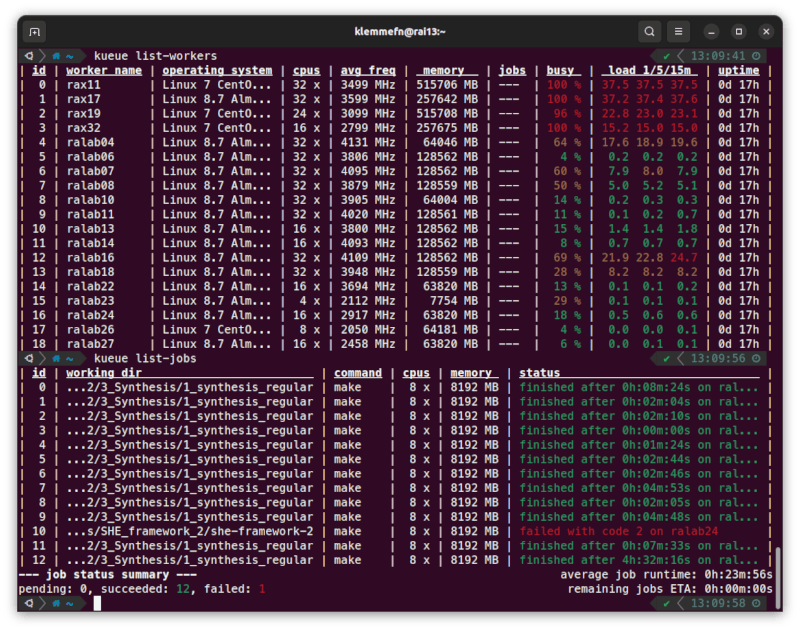
Why Kueue?
Kueue has been developed in a university research environment. Often, scientific experiments are conducted by running commercial tools or custom scripts multiple times, with each execution requiring a certain amount of hardware resources and run time. At the same time, the available computing infrastructure is heterogenous, ranging from a few dedicated servers to a bunch of lab workstations that might reboot from time to time. In such an environment, distributing your workload to different machines can be a cumbersome task: Which machines are currently free? How many jobs can I start/schedule on each machine? Have my scripts completed or did the machine reboot in the meantime?
Kueue tries to alleviate these tasks while keeping the usability as simple as
possible. Its ease of use and the simple configuration is in parts inspired by
Task Spooler, which I have
used for a long time. Running a job with Kueue should be as easy as running it
on the command line on your local machine. In practice, running ./my_script.py
with Kueue on any free machine can be achieved with a simple prefix:
kueue cmd ./my_script.py.
Kueue might be for you, when...
- You only have user privileges on available computing machines.
- A simple command-line interface suffices your needs.
- You are working on machines that reboot or shutdown regularly.
- A simple setup is more important than a rich set of features.
Kueue might not be for you, when...
- You have root privileges and can install an established (multi-user) scheduling system instead.
- You have no shared filesystem and thus need to attach data to your jobs inquiries.
Preparation
Kueue works in a client-server model, which requires the kueue_server to be
running on one machine, and kueue_worker on all machines that should carry out
the execution of jobs. The kueue_server process needs to be reachable on a
(freely specifiable) TCP network port. Similar to the worker, kueue (the
command-line client) connects to the server using the same TCP port on the
server. Authentication is done with a shared_secret that must be identical on
all your machines. Kueue runs completely in user-level mode and all jobs are
executed with the privileges that kueue_worker is started with. Therefore,
make sure not to leak the shared_secret in your config, otherwise other people
can spawn processes on your behalf!
In many infrastructures, /home and other directories are mounted/synchronized
over the network. If the user's home is synced, the configuration at
~/.config/kueue/config.toml can be easily accessed by all processes.
Otherwise, you might need to distribute your config manually to all machines.
All scheduled jobs are executed with respect to their current working directory.
A worker will only execute the job if they can see the same directory (or a
directory with the same path on their system).
Installation
The simplest way to obtain Kueue is by downloading it directly from crates.io. This requires you to install Rust first, which also needs no root privileges if the basic dependencies are already installed. By default, all files will be installed into your home directory. In an environment with synchronized home directories, this means that you usually only need to go through the installation process once.
Installing Rust
Make sure you have a C/C++ compiler installed. Then, install Rust as usual.
curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
Installing OpenSSL
You need to install OpenSSL headers as a dependency of Kueue. On many systems, it might already be installed. On Ubuntu, the following packages will suffice:
sudo apt install pkg-config libssl-dev
On Fedora, the following package solved the missing dependencies:
sudo dnf install openssl-devel
Installing Kueue
Finally, use Cargo (which is included in the Rust installation) to install (or update) Kueue.
cargo install kueue
This will install kueue (the client), kueue_server, and kueue_worker into
the bin folder of your Rust installation.
Basic configuration
Upon the first start of any Kueue binary, a template config file is created at
~/.config/kueue/config.toml. It is worthwile to look at the default settings
and adjust them to your needs. A description of all settings can be found in the
documentation.
The most important settings are in the [common_settings] section. Make sure
that the shared_secret in your config is the same on all systems you want to
use. The same is probably true for server_name and server_port, which is
used by clients and workers to connect to your server.
[common_settings]
shared_secret = "keep private!"
server_name = "ralab29"
server_port = 11236
To get started, run kueue_server on the machine you want to use a the server,
and kueue_worker on all machines you want to execute jobs on. Note that these
programs start in foreground, so you might use a tool like
screen to send the processes to the
background and keep them alive while you're not logged in.
Global resources (e.g. license management)
Kueue can handle "global" resources that must be respected among all workers at
the same time, such as licenses. We demonstrate how to use the feature by
example. To get started, add a new table of resources to your config, named
[global_resources]. Afterward, specify one resource per line, like in the
following example.
[global_resources]
primelib = 31
genus = 3
In this example, we specified two types of licenses and an amount for each
license that can be used by jobs at the same time. Let's assume that
my_script.sh requires one genus license to run. This can be achieve with the
following command:
kueue cmd --resource genus ./my_script.sh
In the following example, our script requires not only one genus license but
also 4 primelib licenses:
kueue cmd --resource genus --resource primelib=4 ./my_script.sh
By providing required global resources accordingly, Kueue can schedule jobs conflict-free.
Restart workers
Kueue comes with a simple tool named kueue_restart_workers that checks the
state of your workers and attempts to restart them if they went down. To use the
tool, add a new block to your config.toml like the following:
[restart_workers]
ssh_user = "klemmefn"
hostnames = """
rax11 rax17 rax19 rax32
ralab04 ralab06 ralab07 ralab08
ralab10 ralab11 ralab13 ralab14
ralab16 ralab18 ralab22 ralab23
ralab24 ralab25 ralab26 ralab27
"""
sleep_minutes_before_recheck = 60
Currently, the tool uses your SSH key to connect to the workers and spawns the worker task in the background using screen. Make sure that screen is installed on your workers and ssh login via key is possible. Then, you can use the tool like this:
# Make sure your SSH key is loaded.
eval `ssh-agent -s`
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
# Spawn "restart_workers" in the background.
screen kueue_restart_workers
Keep in mind that kueue_restart_workers is not required for Kueue to work but
just a simple tool to make restarting workers simpler. You can also use any
other strategy to start and restart your remote workers.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
How do I upgrade to a newer version?
- If you are using
kueue_restart_workerto spawn your worker processes, stop it first. - Stop
kueue_server. This will also terminate all connected worker processes. - Run
cargo install kueueon all your machines (or Kueue installations). If you have a shared home directory, a singlecargo install kueuemight be already sufficient. - After the update has completed, restart
kueue_server. If the server complains about unrecognized setting in you config, read the FAQ below. - Restart your workers, e.g., by starting
kueue_restart_workeragain.
How do I get a new version of the config file (TOML)?
In many cases, an update of the config file is not required when updating Kueue. For any missing setting, a default value is assumed. The default values for all settings can be found in the initial template config file that is generated on first start.
A template config file is create with each start of any kueue binary, if there
is no existing config file in place. Therefore, a simple way to update your
config file is to make a backup (e.g., rename the config file) and simply run
kueue once. Afterwards, compare your backed-up config with the newly create
template and adjust the settings as you like.
I get an error when starting the server!
INFO [kueue_server::server] Successfully started listening on 0.0.0.0:11236...
ERROR [kueue_server::server] Failed to start listening on [::]:11236: Address already in use (os error 98)
The kueue_server supports listening on multiple interfaces, defined in
bind_addresses in the config file. This can be helpful, e.g., if you want to
allow clients to connect either via IPv4 (0.0.0.0) or IPv6 ([::]). The
server will try to bind each address individually with the port specified in
server_port. While this works fine on some systems, other system might
automatically bind both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses if either of 0.0.0.0 or [::]
is present. In this case, you get the above error message because the server
tries to bind the same address twice. You can ignore the message (the server
will still work) or you can fix it by removing one of 0.0.0.0 or [::] from
bind_addresses.
How do I setup shell completion?
The kueue client supports shell completion on the command line with
clap_complete. Calling
kueue complete and the name of your shell as another parameter returns the
completion script for your respective shell. You might evaluate the returned
script directly, or save it to a file and source it afterwards. An easy way
(tested with both bash and zsh) is to put the eval statement directly into
your startup script. For instance, for bash, put
eval "$(kueue complete bash)" into your ~/.bashrc script, and for zsh, put
eval "$(kueue complete zsh)" into your ~/.zshrc script.
Dependencies
~17–32MB
~463K SLoC