32 releases
| new 0.2.2 | May 15, 2024 |
|---|---|
| 0.2.1 | May 14, 2024 |
| 0.1.0 | May 10, 2024 |
| 0.1.0-alpha.7 | Apr 30, 2024 |
| 0.0.2 | Oct 27, 2023 |
#27 in Debugging
1,353 downloads per month
285KB
7.5K
SLoC
tracexec
A small utility for tracing execve{,at} and pre-exec behavior.
tracexec helps you to figure out what and how programs get executed when you execute a command.
It's useful for debugging build systems, understanding what shell scripts actually do, figuring out what programs does a proprietary software run, etc.
Showcases
TUI mode with pseudo terminal
In TUI mode with a pseudo terminal, you can view the details of exec events and interact with the processes within the pseudo terminal at ease.

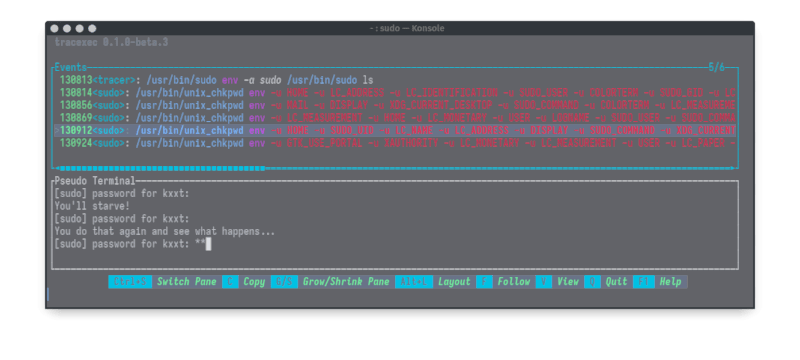
Tracing setuid binaries
With root privileges, you can also trace setuid binaries and see how they work. But do note that this is not compatible with seccomp-bpf optimization so it is much less performant.
sudo tracexec --user $(whoami) tui -t -- sudo ls
Nested setuid binary tracing is also possible: A real world use case is to trace extra-x86_64-build(Arch Linux's build tool that requires sudo):
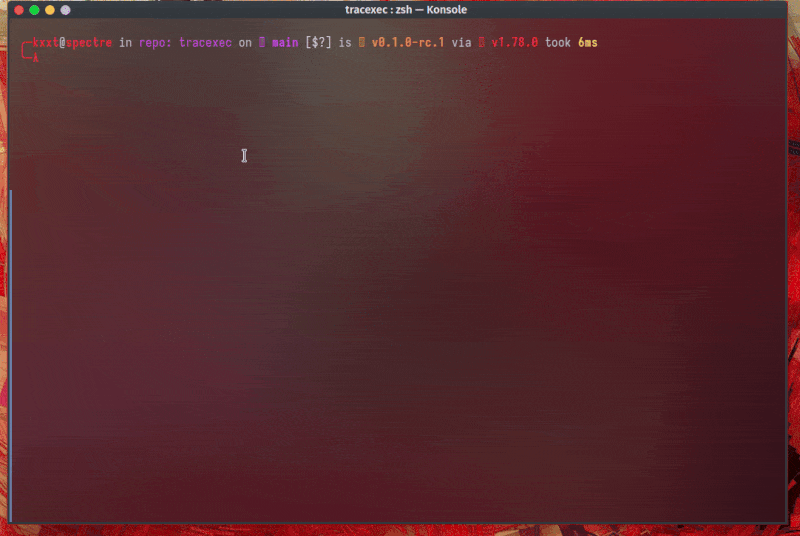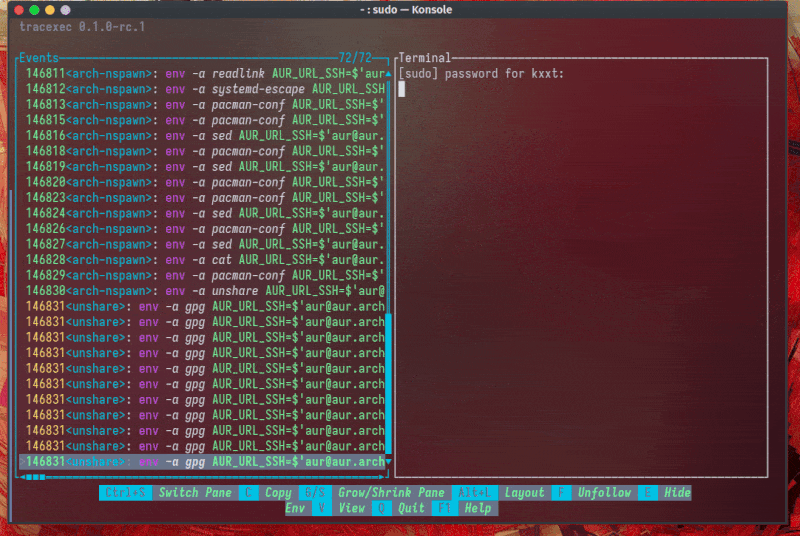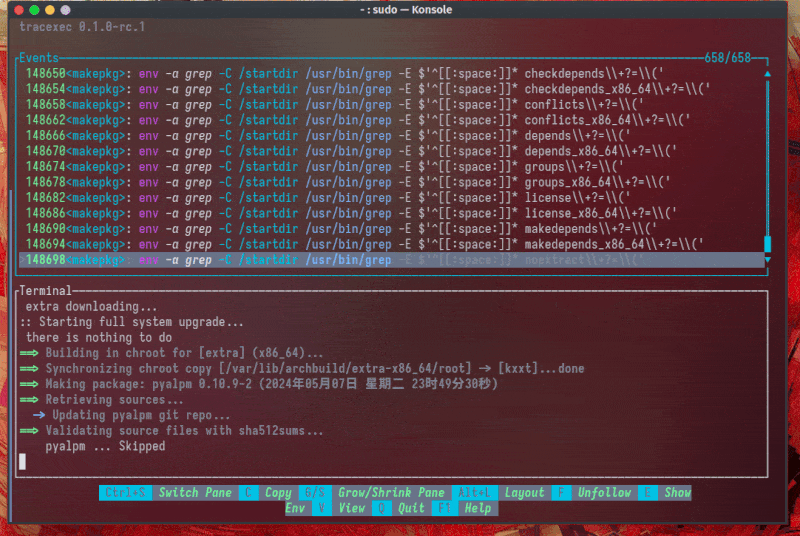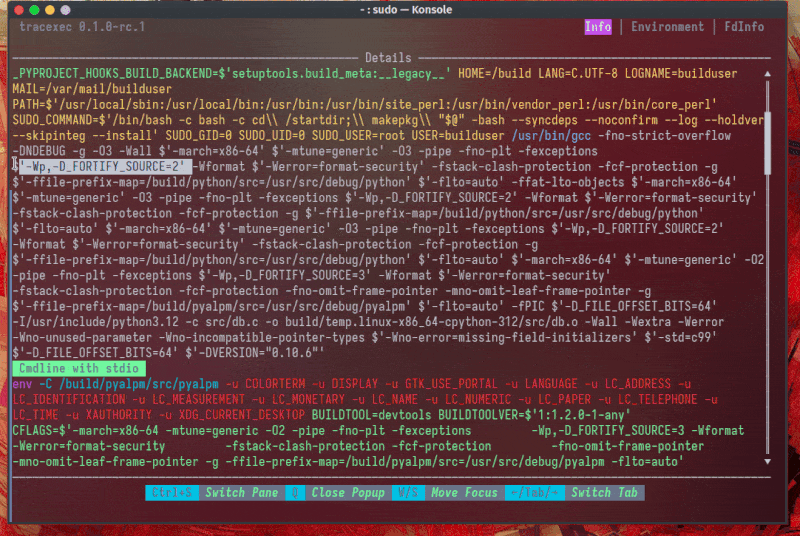
In this real world example, we can easily see that _FORTIFY_SOURCE is redefined from 2 to 3, which lead to a compiler error.
Log mode
In log mode, by default, tracexec will print filename, argv and the diff of the environment variables and file descriptors.
example: tracexec log -- bash (In an interactive bash shell)
Reconstruct the command line with --show-cmdline
$ tracexec log --show-cmdline -- <command>
# example:
$ tracexec log --show-cmdline -- firefox
Try to reproduce stdio in the reconstructed command line
--stdio-in-cmdline and --fd-in-cmdline can be used to reproduce(hopefully) the stdio used by a process.
But do note that the result might be inaccurate when pipes, sockets, etc are involved.
tracexec log --show-cmdline --stdio-in-cmdline -- bash
Show the interpreter indicated by shebang with --show-interpreter
And show the cwd with --show-cwd.
$ tracexec log --show-interpreter --show-cwd -- <command>
# example: Running Arch Linux makepkg
$ tracexec log --show-interpreter --show-cwd -- makepkg -f
Installation
From source
Via cargo:
cargo install tracexec --bin tracexec
Arch Linux users can also install from the official repositories via pacman -S tracexec.
Binary
You can download the binary from the release page
Usage
General CLI help:
A small utility for tracing execve{,at} and pre-exec behavior
Usage: tracexec [OPTIONS] <COMMAND>
Commands:
log Run tracexec in logging mode
tui Run tracexec in TUI mode, stdin/out/err are redirected to /dev/null by default
help Print this message or the help of the given subcommand(s)
Options:
--color <COLOR> Control whether colored output is enabled. This flag has no effect on TUI mode. [default: auto] [possible values: auto, always, never]
-C, --cwd <CWD> Change current directory to this path before doing anything
-u, --user <USER> Run as user. This option is only available when running tracexec as root
-h, --help Print help
-V, --version Print version
TUI Mode:
Run tracexec in TUI mode, stdin/out/err are redirected to /dev/null by default
Usage: tracexec tui [OPTIONS] -- <CMD>...
Arguments:
<CMD>... command to be executed
Options:
--seccomp-bpf <SECCOMP_BPF>
seccomp-bpf filtering option [default: auto] [possible values: auto, on, off]
--successful-only
Only show successful calls
--fd-in-cmdline
[Experimental] Try to reproduce file descriptors in commandline. This might result in an unexecutable cmdline if pipes, sockets, etc. are involved.
--stdio-in-cmdline
[Experimental] Try to reproduce stdio in commandline. This might result in an unexecutable cmdline if pipes, sockets, etc. are involved.
--show-all-events
Set the default filter to show all events. This option can be used in combination with --filter-exclude to exclude some unwanted events.
--filter <FILTER>
Set the default filter for events. [default: warning,error,exec,tracee-exit]
--filter-include <FILTER_INCLUDE>
Aside from the default filter, also include the events specified here. [default: <empty>]
--filter-exclude <FILTER_EXCLUDE>
Exclude the events specified here from the default filter. [default: <empty>]
-t, --tty
Allocate a pseudo terminal and show it alongside the TUI
-f, --follow
Keep the event list scrolled to the bottom
--terminate-on-exit
Instead of waiting for the root child to exit, terminate when the TUI exits
--kill-on-exit
Instead of waiting for the root child to exit, kill when the TUI exits
-A, --active-pane <ACTIVE_PANE>
Set the default active pane to use when TUI launches [default: terminal] [possible values: terminal, events]
-L, --layout <LAYOUT>
Set the layout of the TUI when it launches [default: horizontal] [possible values: horizontal, vertical]
-F, --frame-rate <FRAME_RATE>
Set the frame rate of the TUI [default: 60.0]
-h, --help
Print help
Log Mode:
Run tracexec in logging mode
Usage: tracexec log [OPTIONS] -- <CMD>...
Arguments:
<CMD>... command to be executed
Options:
--show-cmdline
Print commandline that (hopefully) reproduces what was executed. Note: file descriptors are not handled for now.
--show-interpreter
Try to show script interpreter indicated by shebang
--more-colors
More colors
--less-colors
Less colors
--diff-fd
Diff file descriptors with the original std{in/out/err}
--no-diff-fd
Do not diff file descriptors
--show-fd
Show file descriptors
--no-show-fd
Do not show file descriptors
--diff-env
Diff environment variables with the original environment
--no-diff-env
Do not diff environment variables
--show-env
Show environment variables
--no-show-env
Do not show environment variables
--show-comm
Show comm
--no-show-comm
Do not show comm
--show-argv
Show argv
--no-show-argv
Do not show argv
--show-filename
Show filename
--no-show-filename
Do not show filename
--show-cwd
Show cwd
--no-show-cwd
Do not show cwd
--decode-errno
Decode errno values
--no-decode-errno
--seccomp-bpf <SECCOMP_BPF>
seccomp-bpf filtering option [default: auto] [possible values: auto, on, off]
--successful-only
Only show successful calls
--fd-in-cmdline
[Experimental] Try to reproduce file descriptors in commandline. This might result in an unexecutable cmdline if pipes, sockets, etc. are involved.
--stdio-in-cmdline
[Experimental] Try to reproduce stdio in commandline. This might result in an unexecutable cmdline if pipes, sockets, etc. are involved.
--show-all-events
Set the default filter to show all events. This option can be used in combination with --filter-exclude to exclude some unwanted events.
--filter <FILTER>
Set the default filter for events. [default: warning,error,exec,tracee-exit]
--filter-include <FILTER_INCLUDE>
Aside from the default filter, also include the events specified here. [default: <empty>]
--filter-exclude <FILTER_EXCLUDE>
Exclude the events specified here from the default filter. [default: <empty>]
-o, --output <OUTPUT>
Output, stderr by default. A single hyphen '-' represents stdout.
-h, --help
Print help
The recommended way to use tracexec is to create an alias with your favorite options in your bashrc:
alias tracex='tracexec log --show-cmdline --show-interpreter --show-children --show-filename --'
alias txtui='tracexec tui -t --'
# Now you can use
tracex <command>
txtui <command>
Known issues
- Non UTF-8 strings are converted to UTF-8 in a lossy way, which means that the output may be inaccurate.
- The output is not stable yet, which means that the output may change in the future.
- Test coverage is not good enough.
- The pseudo terminal can't pass through certain key combinations and terminal features.
Origin
This project was born out of the need to trace the execution of programs.
Initially I simply use strace -Y -f -qqq -s99999 -e trace=execve,execveat <command>.
But the output is still too verbose so that's why I created this project.
Credits
Dependencies
~24–40MB
~602K SLoC